Causes of Mass Wasting - Gravity
 |
A bit of physics: Resisting forces = Material strength. So, the stronger the material strength, the stronger the resisting force. However, cohesion and friction also play a role in slope stability. The steeper the slope, the larger the resistance force will need to be to prevent failure. |
Water
Mass wasting events can be triggered when water builds up in the slope heavy rains. This can be due to snowmelt, heavy rains, or poor drainage.When water builds up in a slope several things can occur. First, water > the weight and < the strength of the material in the slope. Pore pressure in the slope >, and clay minerals become hydrated and expand. Minerals holding individual grains together may dissolve.

Weather comes in cycles with dry periods of 15 years and wet of 12 years. The greater the storm frequency, intensity, and duration the greater the hillside damage. During periods of heavy rainfall, hills can become become pocked with soil failures.
Drainage systems are needed for some slopes in construction areas or new developments. Impermeable surfaces can cause excess runoff, which can lead to erosion and slope failure.
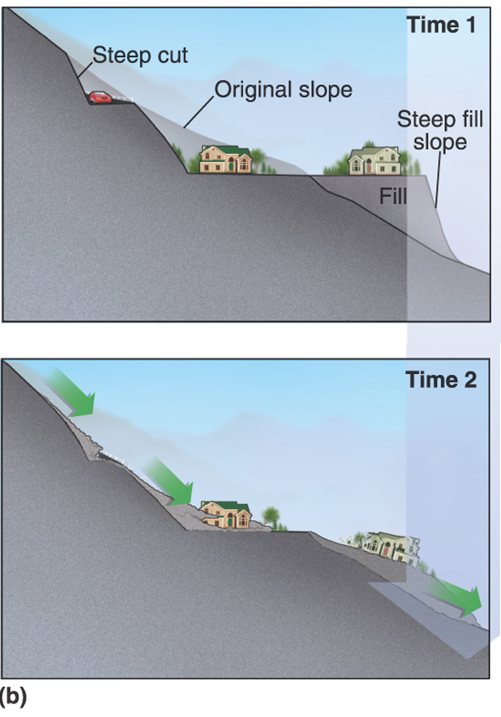
Steep Slopes
Slopes fail occur when gravitational forces exceed the strength of the rock or soil which comprise the slope. This often occurs when a slope is over steepened, a heavy load is placed at the top of the slope, or material at the base of the slope is removed.
 |
 |
| Oversteepened slope failure | Undermining / toe removal failure |
Vegetation
The type of vegetation present (or not) on a slope can affect slope stability. Plants with deep roots hold bedrock and loose materials together. Shallow-rooted plants provide stability for soils and other surficial deposits. Slope stability can be affected if vegetation is removed. Reseeding or replanting slopes of questionable stability is often recommended.Geology
The geology of a region greatly affects slope stability.Adverse Geological Structure
Bedding surfaces of weak rocks dip downslope and are unsupported at the lower end . Similar problems can occur with faults, joints, foliation etc

Weak Rocks
- Many Southern California rocks are rich in clay or silt. Clays like montmorillonite swells in water & disintegrates, undermining the stability of the rocks. Clays may cause instability on a 5º slope.
Interbedding of sandstone and clay is a common problem in some areas.
Serpentine, the state rock, causes many landslides
Quick clays are the most mobile of all deposits – fine rock flour scoured by glaciers, deposited in seas and later exposed above water. The salts that are helping to hold the clay together dissolve in water, causing the slope to fail.

Earthquakes
Earthquakes, or any other type of strong vibrations, can trigger landsides on slopes which are already unstable. In general, only earthquakes that are a magnitude 4.0 or greater will be strong enough to cause a slide.
Human caused Landslides
Four ways to make a stable slope unstable- Steepen slope angle
- Increase the height of the slope
- Saturate with water
- Place an extra load on the slope
<< back |
||
